Navigating Industry 4.0: AGV vs AMR - A Comprehensive Guide
Curious about the optimal choice between Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) and Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) for your business in Industry 4.0? Which one is the best fit for your company’s needs? Let’s delve deep into the comparison between AGVs and AMRs, considering both technical aspects and practical applications to help you make an informed decision.
Understanding the Difference
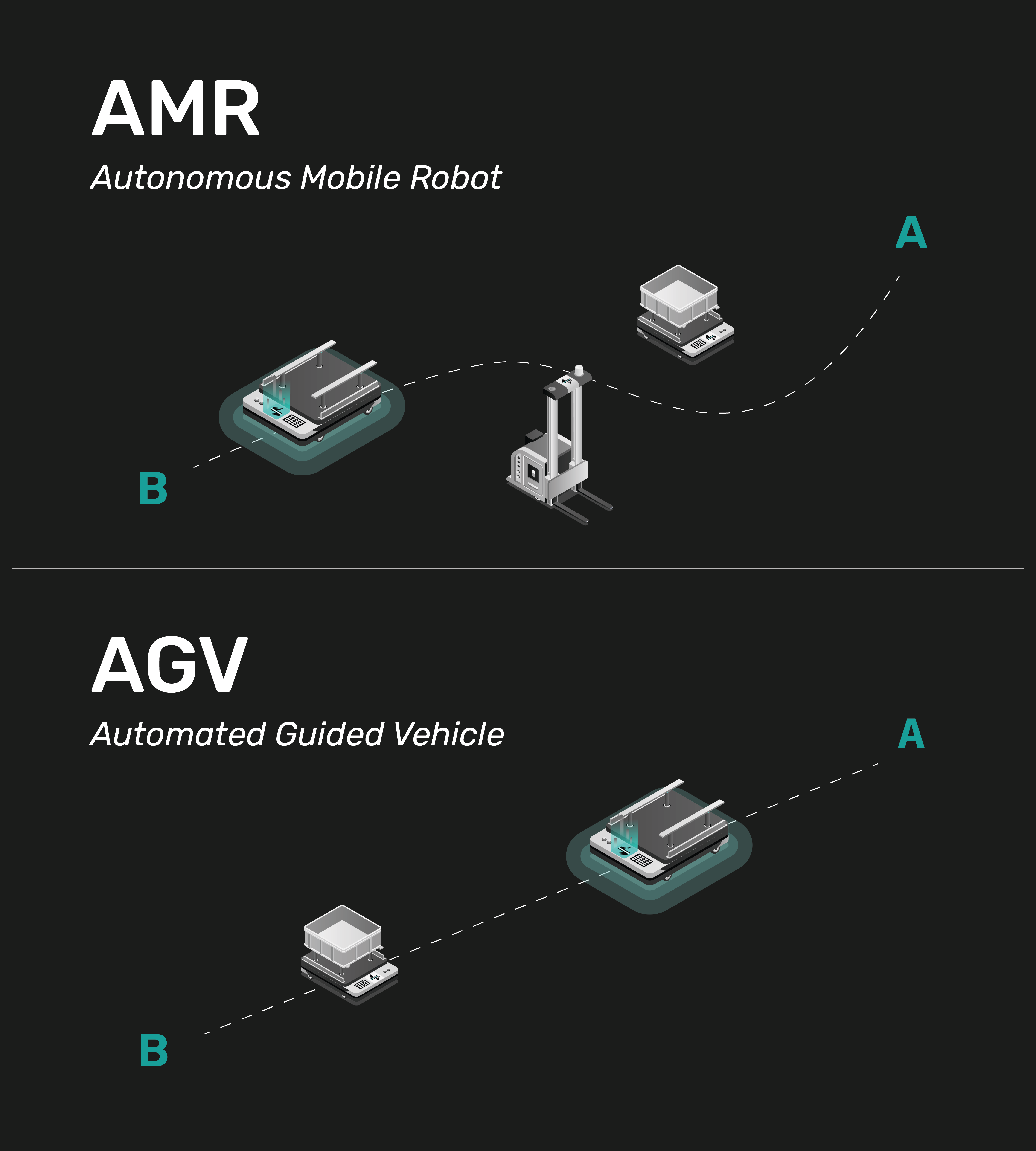
AGVs and AMRs may appear similar at first glance, but they operate on fundamentally different principles, particularly in terms of navigation, flexibility, applications, and capabilities. Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) follow predefined paths within controlled environments, relying on guidance devices such as wires, magnets, or lasers. They excel in point-to-point transport tasks and are robust solutions for fixed route material delivery. Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs), on the other hand, leverage sophisticated onboard sensing and artificial intelligence for autonomous navigation. They dynamically navigate through changing warehouse environments without the need for fixed pathways or external infrastructure. AMRs integrate seamlessly with human workers and processes, offering versatility in material transport tasks like picking and conveyor integration.
Understanding the Technical Nuances
Navigation Systems
AGVs: Employ predefined guidance systems such as wires, magnets, barcodes, or lasers to follow fixed pathways within controlled environments. These systems dictate the route and movement of AGVs, ensuring precise navigation along predetermined routes.
AMRs: Rely on advanced onboard sensing technologies, including LiDAR, cameras, and depth sensors, coupled with artificial intelligence algorithms for autonomous navigation. AMRs create dynamic maps of their surroundings and utilize real-time data to navigate through complex environments without the need for fixed pathways or external guidance systems.
Flexibility and Adaptability
AGVs: Suited for applications in environments with stable layouts and predictable traffic patterns. AGVs operate efficiently within predefined routes and are less adaptable to changes in operational conditions or layout modifications.
AMRs: Excel in dynamic and evolving environments, offering unparalleled flexibility and adaptability. With their ability to dynamically navigate through changing layouts and obstacles, AMRs can seamlessly adjust their routes and operational parameters to accommodate evolving operational requirements.
Task Complexity and Versatility
AGVs: Primarily designed for repetitive point-to-point material transport tasks within controlled spaces. While AGVs excel in simple material handling operations, they are limited in their ability to perform complex tasks or adapt to diverse operational requirements.
AMRs: Versatile and multifunctional, AMRs can handle a wide range of material handling tasks, including picking, sorting, replenishment, and collaborative interactions with human operators. Their advanced sensing and navigation capabilities enable AMRs to navigate through dynamic environments and execute complex tasks with precision and efficiency.
Integration and Compatibility
AGVs: Typically require infrastructure modifications and dedicated pathways for operation. Integration with existing systems may require additional hardware or software adaptations to ensure seamless communication and coordination within the overall automation ecosystem.
AMRs: Offer greater compatibility and interoperability with existing systems and workflows. AMRs can easily integrate with warehouse management systems (WMS), enterprise resource planning (ERP) software, and other automation technologies, facilitating seamless data exchange and coordination across the entire supply chain.
Making the Right Choice for Your Business
When evaluating the technical specifications of AGVs and AMRs, several factors must be considered to determine the optimal solution for your business:
Operational Environment: Assess the complexity, variability, and layout dynamics of your facility to determine the suitability of AGVs or AMRs. AGVs may be well-suited for controlled environments with fixed routes, while AMRs offer greater adaptability to dynamic operational conditions.
Task Complexity: Consider the range of material handling tasks involved in your operations and evaluate the capabilities of AGVs and AMRs to meet your specific requirements. If your operations involve complex tasks or require versatile automation solutions, AMRs may offer a more suitable option.
Integration and Compatibility: Evaluate the compatibility of AGVs or AMRs with existing systems, workflows, and automation technologies. Choose a solution that seamlessly integrates with your existing infrastructure and facilitates efficient communication and coordination within your automation ecosystem.
AGVs
If your company requires robust material transport solutions for fixed routes in controlled environments, AGVs may be the better choice. They are cost-effective, reliable, and well suited for repetitive tasks without significant environmental changes. AGVs are ideal for businesses with stable processes and infrastructure.
AMRs
For companies seeking greater flexibility, adaptability, and scalability in material handling operations, AMRs offer a compelling solution. Their autonomous navigation capabilities enable them to navigate dynamic environments efficiently, making them suitable for industries with evolving processes and layouts. AMRs integrate seamlessly with existing workflows and can be easily redeployed to accommodate changing demands.
In summary, the choice between AGVs and AMRs depends on your company’s specific requirements, goals, and operational environment. While AGVs excel in fixed route material transport within controlled spaces, AMRs offer unparalleled flexibility and adaptability to dynamic warehouse environments. For many businesses, a combination of both technologies may provide the optimal solution, leveraging the strengths of each to enhance overall efficiency and productivity.
Why Choose If You Can Have Both?
At NODE, we recognize that the decision between AGVs and AMRs can be challenging, as each technology offers unique advantages. However, we believe that with the right software solution, it's possible to bridge the gap between AGVs and AMRs, allowing businesses to leverage the benefits of both technologies simultaneously.
Introducing NODE.OS
Our proprietary software solution, NODE.OS, empowers users to customize the autonomy levels of AMRs, effectively blurring the lines between traditional AGVs and advanced robotics. With NODE.OS, an AMR can be tailored to behave like an AGV in certain scenarios, while still retaining its inherent flexibility and adaptability.
How Does it Work?
NODE.OS enables users to program AMRs to follow predetermined rules in specific areas or environments, mimicking the behavior of AGVs when necessary. This functionality provides businesses with the flexibility to optimize their material handling processes according to task requirements and operational conditions. The good news is that modern AGVs are already equipped with the hardware necessary to support advanced autonomy features. By leveraging NODE.OS, businesses can easily upgrade their existing AGVs to configurable AMRs, maximizing the versatility and efficiency of their automation systems.
Embrace the Best of Both Worlds
With NODE.OS, there's no need to compromise between AGVs and AMRs. By combining the reliability of AGVs with the adaptability of AMRs, businesses can achieve optimal efficiency, productivity, and scalability in their material handling operations. Reach out to our team to learn more about the configurable autonomy functions offered by NODE.OS. From continuous map updates to collaborative path planning, NODE.OS provides a comprehensive suite of features designed to enhance the performance and flexibility of your AGVs and AMRs.
TL;DR
The comprehensive guide explores the choice between Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) and Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) in Industry 4.0, focusing on their operational disparities in navigation methods, flexibility, task complexity, and integration with existing systems. AGVs adhere to fixed paths in controlled environments, whereas AMRs navigate autonomously using advanced sensors and AI algorithms. While AGVs suit stable layouts, AMRs adapt well to dynamic environments. Considerations such as task complexity and integration compatibility are crucial in selecting the right solution. However, NODE.OS software offers a hybrid approach by allowing AMRs to emulate AGV behavior, blending the advantages of both technologies to optimize material handling operations for efficiency and scalability.
Visit www.node-robotics.com for more information.